Step back in time and immerse yourself in the captivating world of the Mesozoic Era – a period renowned for its fascinating prehistoric beasts. This post is an intriguing journey into an epoch where dinosaurs roamed the Earth, and every day was a battle for survival. 🦖🌍
Prepare to delve deep into a period characterized by the rise and fall of some of the most spectacular creatures the world has ever seen. From the colossal Brachiosaurus to the ferocious Tyrannosaurus Rex, every creature has a story to tell. Through a detailed exploration of their lives, habitats, and unique adaptations, you’ll gain a new appreciation for these magnificent beasts. 🦕🌴
This comprehensive overview of the Mesozoic Era will provide invaluable insights and exciting revelations about the world as it was millions of years ago. So, let’s unleash the roar of prehistoric beasts and delve into an unforgettable adventure through the annals of Earth’s history. 🌋🐾
The Mesozoic Era: An Overview
The Mesozoic Era, spanning from about 252 to 66 million years ago, is often referred to as the “Age of Dinosaurs.” It’s divided into three distinct periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous. This era witnessed the emergence and extinction of some of the most iconic prehistoric creatures that ever roamed the planet.
The transition into the Mesozoic Era followed the Permian-Triassic extinction event, the most severe extinction in Earth’s history, which wiped out nearly 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrates. From this devastation emerged new life forms that would go on to dominate Earth for over 180 million years. The Mesozoic was a time of significant geological and biological change, marked by the gradual breakup of the supercontinent Pangea, which shaped the climate, ocean currents, and biodiversity patterns across the globe.
During the Triassic Period, life was recovering and diversifying, setting the stage for the rise of reptiles, including the earliest dinosaurs and marine reptiles. This period also saw the first appearance of mammals and early pterosaurs, the flying reptiles of the skies.
The Jurassic Period marked the height of dinosaur diversity and the flourishing of lush forests and giant ferns. It was during this time that the first birds appeared, evolving from small feathered dinosaurs, providing a critical evolutionary link.
By the Cretaceous Period, flowering plants had begun to spread, drastically changing ecosystems. Iconic dinosaurs like the Tyrannosaurus rex, Velociraptor, and Triceratops roamed the Earth, while the oceans teemed with colossal marine reptiles and ammonites. The Mesozoic Era ultimately ended with the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event, most likely caused by a massive asteroid impact, which brought an end to the reign of the dinosaurs and cleared the path for mammals to rise.
The Triassic Period
The Triassic Period, occurring approximately 252 to 201 million years ago, marks the beginning of the Mesozoic Era and a new chapter in Earth’s evolutionary history. It followed the devastating Permian-Triassic extinction event, which eradicated most life on the planet. In the wake of this mass extinction, new life began to flourish, setting the stage for the rise of the dinosaurs and many other prehistoric creatures.
One of the defining features of the Triassic world was the supercontinent Pangea, a massive landmass that brought all the Earth’s continents together into one. This configuration had profound effects on the global climate. Much of the interior of Pangea was arid and dry, with extreme seasonal temperature fluctuations. These harsh conditions influenced the evolution of plants and animals, favoring those capable of surviving in drier, more variable environments.
Vegetation during this time was dominated by gymnosperms such as cycads, conifers, and ginkgoes. These plants formed the foundation of the food chain and provided the basis for the terrestrial ecosystems in which reptiles began to thrive. Amphibians were still relatively common, but it was the reptiles—especially the early archosaurs—that would come to dominate.
Among the first true dinosaurs to appear were small, lightly built, bipedal predators like Eoraptor e Herrerasaurus, which lived toward the end of the Triassic. Although these early dinosaurs were not the dominant life forms of their time, they paved the way for the immense diversity of dinosaurs that would follow in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
Marine life also saw significant developments. The oceans were populated by an array of marine reptiles, including the sleek and agile Ichthyosaurus, which resembled modern dolphins in both form and lifestyle. These creatures were well-adapted to life in the sea, using their streamlined bodies and powerful tails to chase down fish and squid.
Other notable Triassic reptiles included the Plateosaurus, a large herbivore with a long neck and tail that could walk on two or four legs. Although not a true dinosaur by modern classification, it was among the earliest members of the sauropodomorph lineage, which would eventually give rise to the gigantic long-necked dinosaurs of the Jurassic.
The Triassic Period was a time of experimentation and recovery, a critical foundation upon which the dinosaur dynasty was built. It was a world of evolutionary firsts, setting the tone for the dramatic rise of the reptiles in the ages to come.
The Jurassic Period
Following the Triassic is the Jurassic period, spanning from 201 to 145 million years ago. It’s during this period that dinosaurs truly dominated, evolving into a vast array of shapes and sizes.
Standout creatures from the Jurassic period include the Brachiosaurus, a giant long-necked dinosaur, and the Stegosaurus, famed for its plated back and spiked tail.
Diving Deeper into Mesozoic Creatures
Unleashing the roar of these prehistoric beasts, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating creatures that inhabited the Earth during the Mesozoic Era.
The Tyrannosaurus Rex
Perhaps the most iconic dinosaur of all, the Tyrannosaurus Rex—often simply called T. rex—hailed from the late Cretaceous period, approximately 68 to 66 million years ago. Towering at nearly 12 feet tall at the hips and measuring up to 40 feet in length, the T. rex was one of the largest land carnivores to ever walk the Earth. Its name, which means “tyrant lizard king,” perfectly encapsulates its fearsome reputation.
One of the most striking features of T. rex was its massive skull, which could measure over 5 feet long. Equipped with powerful jaw muscles, it delivered one of the strongest bite forces of any known terrestrial animal—estimated to be over 6 tons. Its teeth, some as long as bananas, were thick, serrated, and adapted for crushing bone. Unlike many predators that sliced flesh cleanly, the T. rex was capable of pulverizing bones to access the nutrient-rich marrow within—a behavior supported by fossil evidence of crushed bone fragments in its coprolites (fossilized droppings).
Despite its ferocious bite and towering size, the T. rex is often the subject of curiosity due to its tiny forelimbs. These two-fingered arms were unusually short for an animal of such size, but they were far from useless. Studies suggest they were strong and muscular, possibly used to grip prey during feeding or assist the dinosaur in getting up from a resting position. The debate over their function continues, but it’s clear they were not mere evolutionary leftovers.
T. rex likely led an active predatory lifestyle, though some paleontologists propose it may have also scavenged when the opportunity arose. With keen senses, especially its exceptional sense of smell—thanks to enlarged olfactory bulbs—it could detect prey or carrion from miles away. Its binocular vision and depth perception were also highly developed, giving it an advantage as both a hunter and scavenger.
Fossil discoveries, including nearly complete skeletons and fossilized skin impressions, have allowed scientists to reconstruct much of T. rex’s biology. Some recent studies even suggest that it may have been covered in feathers during some stage of its life, particularly as a juvenile—a detail that reshapes how we envision this ancient predator.
As the last of the non-avian dinosaurs, Tyrannosaurus rex disappeared during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, ending its reign as apex predator. Yet its legacy endures, not just in science, but in popular culture, where it remains a symbol of prehistoric power and evolutionary intrigue.
The Triceratops
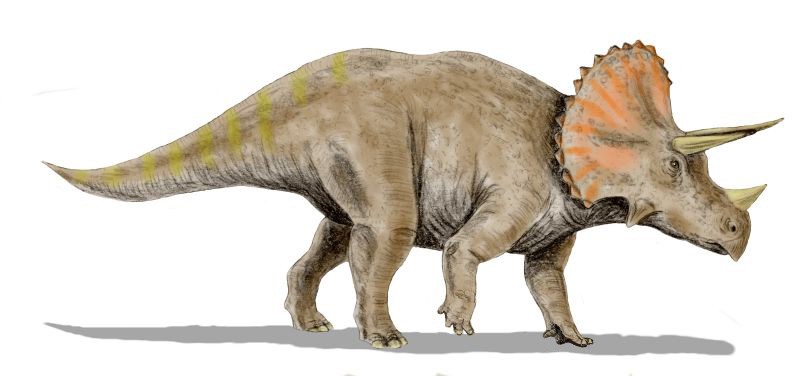
Another standout from the Cretaceous period is the Triceratops. Recognizable by its three-horned face, the Triceratops was a herbivore, feeding on low-growing plants.
The Mesozoic Marine Life
The Mesozoic era also saw the evolution of unique marine creatures, as the warm, shallow seas provided a conducive environment for their development.
The Plesiosaurus
O Plesiosaurus was a marine reptile with a long neck and four large paddle-like limbs. These creatures were likely ambush predators, using their long necks to strike quickly at unsuspecting prey.
The Mosasaurus

O Mosasaurus was a formidable marine predator. These massive aquatic lizards had powerful jaws capable of crushing prey, making them one of the ocean’s apex predators.
The Mesozoic Era: A Time of Rapid Evolution
The Mesozoic era was characterized by rapid evolution and the emergence of some of the most fascinating creatures to ever inhabit the Earth. From the towering dinosaurs to the unique marine reptiles, this era left an indelible mark on the planet’s history.
The Evolution of Birds
One of the significant events of the Mesozoic era was the evolution of birds. The Archaeopteryx is widely regarded as the first bird, showcasing features of both dinosaurs and modern birds.
The End of an Era
The Mesozoic era ended with the mass extinction event known as the K-T Event, where a large asteroid or comet struck the Earth. This catastrophic event led to the extinction of approximately 75% of all species, including the dinosaurs.
Mesozoic Creatures in Popular Culture
These prehistoric creatures have captivated the human imagination, leaving a lasting impression on popular culture. From books to films, their legacy continues to thrive and inspire.
Dinosaurs in Film
One of the most notable examples of dinosaurs in popular culture is the “Jurassic Park” series. This iconic film franchise brought these extinct creatures to life, making them household names.
Prehistoric Creatures in Literature
In literature, prehistoric creatures are often featured in works of science fiction and fantasy. Books like “The Lost World” by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle and “Raptor Red” by Robert T. Bakker offer engaging tales of these fascinating beasts.
The Legacy of the Mesozoic Era
The Mesozoic era, with its array of prehistoric creatures, has left a profound impact on our understanding of life’s history. These magnificent creatures continue to inspire and captivate us, serving as a testament to Earth’s dynamic and ever-changing nature.
The Importance of Paleontology
Paleontology, the study of ancient life, plays a vital role in deciphering the secrets of the Mesozoic era. Through the tireless work of paleontologists, we’ve been able to unearth a wealth of knowledge about these prehistoric creatures, enriching our understanding of the Earth’s history.
The Enduring Fascination with Dinosaurs
Despite their extinction millions of years ago, dinosaurs continue to fascinate us. Whether it’s their sheer size, diverse forms, or their ultimate demise, these creatures hold a special place in our collective consciousness. They serve as a reminder of our planet’s vibrant past and the intricate web of life that has unfolded over millions of years.
Conclusão
In conclusion, delving into the Mesozoic Era and the fascinating creatures that inhabited our planet during that time is an adventure filled with excitement, wonder, and discovery. These prehistoric beasts, with their thunderous roars and imposing stature, have the power to captivate our imaginations and stir up our curiosity, inspiring us to delve deeper into the mysteries of the natural world. Whether it’s the swift and deadly Velociraptor, the massive and intimidating Tyrannosaurus Rex, or the gentle and herbivorous Triceratops, each creature offers a glimpse into a past world that is vastly different from our own. Understanding their ways of life, their struggles, and their triumphs, can offer us valuable insights into the evolution of life on earth and our own place within it. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of biodiversity and the preservation of our natural habitats. So, let’s unleash the roar of these prehistoric beasts, embark on this thrilling journey into the Mesozoic Era, and uncover the fascinating stories these creatures have to tell. Their legacy, after all, continues to shape the world we live in today.



